A Comprehensive Reasoning Framework for Hardware Refresh in Data Centers
In the realm of data centres, the concept of hardware refresh, particularly in large-scale facilities, has garnered significant attention due to its potential impact on energy efficiency and the broader environmental footprint. This understanding leads to an in-depth exploration of the optimal timing for hardware refresh in data centres, considering the complex interplay between energy savings and environmental impacts.
Understanding Hardware Refresh in Data Centers
Data centres, crucial to our digital economy and social well-being, have become notable for their energy consumption and environmental impact. With an increasing trend toward consolidating computing in larger facilities, such as in cloud computing, smart cities, and IoT, data centres’ energy consumption has been a rising concern. This is further complicated by the frequent refresh of IT hardware in hyper-scale data centres, prompting questions about the wider environmental impact of such practices.
Methodology for Optimizing Hardware Refresh
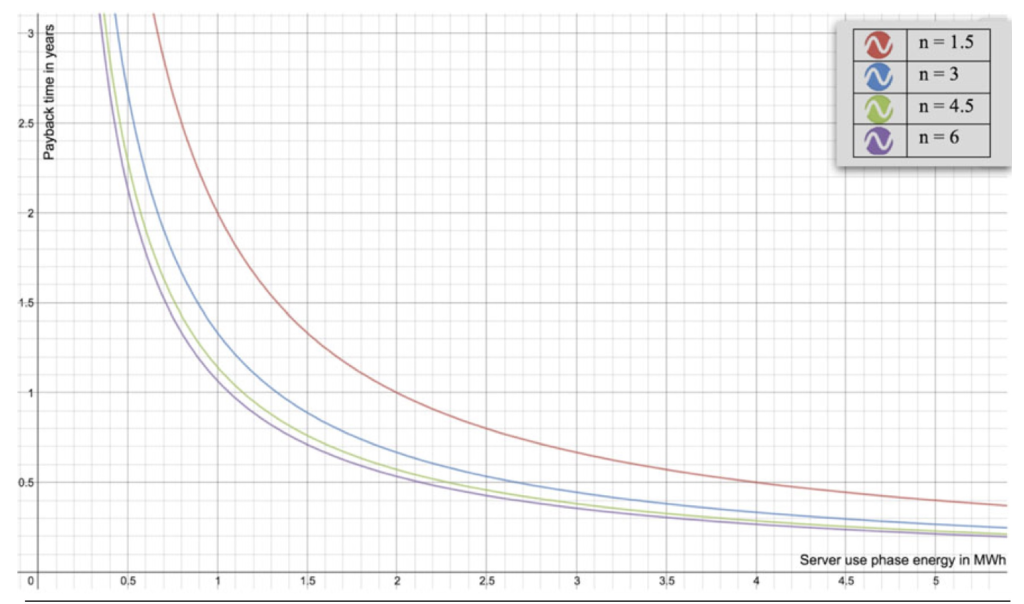
The approach outlined proposes a methodology to calculate the potential use phase energy savings due to hardware refresh, factoring in the server’s embodied energy (the energy consumed to produce the hardware) while excluding broader life cycle energy elements to maintain simplicity. This methodology is crucial in determining the optimal time interval for hardware refresh, which can lead to significant energy savings and reduced environmental impacts.
Case Studies and Real-Life Applications
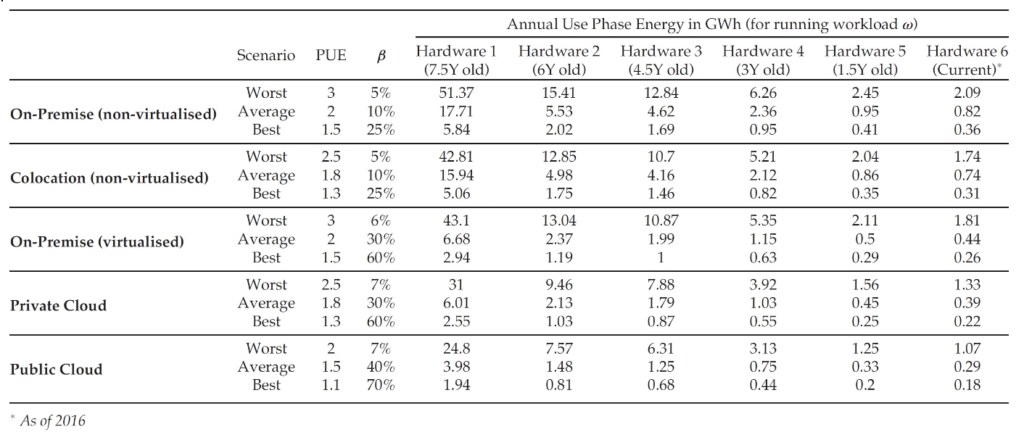
Through various case studies based on real-life data, the concepts are validated, demonstrating the energy-saving opportunities and the overall environmental impact related to hardware refresh. These case studies use different data centre deployment scenarios to illustrate how the proposed framework can be applied in practical settings.
The Environmental Angle
One of the critical aspects of this approach is its consideration of the wider Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) environmental analysis. This analysis is essential in demonstrating that decisions based on the reasoning framework lead to not only energy savings but also a reduction in the overall environmental impact. The LCA approach considers the environmental impact of the manufacturing, transport, usage, and end-of-life of equipment, providing a comprehensive view of a hardware’s environmental footprint.
Implications and Conclusion
The findings highlight the importance of considering both energy efficiency and environmental impact in data centre hardware refresh decisions. This approach challenges the industry’s traditional focus on metrics like Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) and emphasizes a more holistic view of data centre efficiency, one that incorporates the environmental impacts of hardware refreshes. The methodology and case studies offer valuable insights for data centre operators and IT professionals, providing a framework to make more informed decisions about hardware refresh strategies that balance energy efficiency with environmental sustainability.
In summary, this comprehensive framework and its application in real-world scenarios mark a significant step towards more sustainable and efficient data centre operations. By focusing on the entire life cycle of IT hardware and considering both energy and environmental impacts, data centre operators can make more informed decisions that align with broader sustainability goals.