Architectural Principles for Energy-Aware Internet-Scale Applications
In today’s digital age, where software applications consume nearly 10% of the world’s electricity, there’s a pressing need to address the energy efficiency of these systems. This concern is amplified by the fact that while data centres and hardware have seen significant improvements in energy efficiency, software systems lag behind. This gap calls for a system-wide approach to energy efficiency in software engineering.
The Evolution of Energy Efficiency
A decade of progress in enhancing IT infrastructure efficiency, particularly in data centres, has led to improved Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE). However, optimizing the energy efficiency of software systems as a whole remains a challenge. Unlike hardware, where energy consumption can be more straightforwardly measured and optimized, software applications present unique challenges due to their complex, multi-platform nature.
Architectural Principles for Energy Efficiency
To address these challenges, a set of architectural principles is proposed, focusing on energy-aware internet-scale applications:
- Business Transactions Alignment with Energy Consumption: It’s crucial to measure energy efficiency in a manner that aligns with key system stakeholders, linking business transactions to energy consumption. This approach ensures that energy efficiency resonates with the broader goals of the organization.
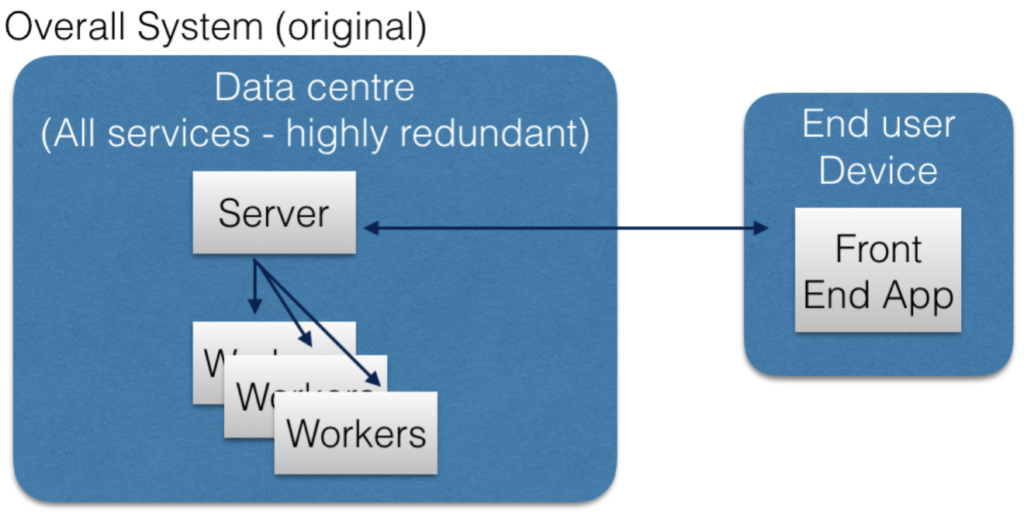
- System-Level Energy Waste Identification: The most significant energy savings are achieved by addressing energy waste at the system level, rather than just focusing on individual components. This requires a comprehensive understanding of the entire system’s energy footprint.
- Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration: Tackling energy optimization in software systems demands collaboration across various specialities. This includes transcending traditional boundaries in design and development to include perspectives from different areas of expertise.
Practical Application: The eBay Case
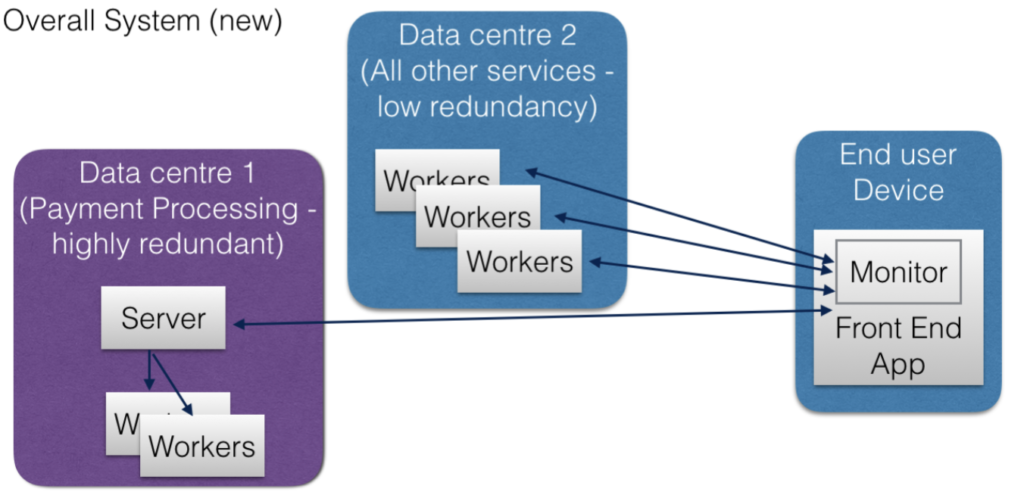
eBay serves as a prime example of successfully applying these principles. By rethinking its system architecture with a focus on energy efficiency, eBay achieved a remarkable 50% reduction in energy consumption. This was accomplished through innovative approaches to system resilience, redundancy, and energy consumption, demonstrating the effectiveness of a holistic view of system architecture.